16/07/2025
Precision Control of Laser Form and Profile Files in 3D Metal Printers
As the boundaries of technology continue to expand, 3D metal printers are revolutionizing the worlds of industry, construction, and art. In particular, the use of laser technology in generating form and profile files stands out as one of the most critical elements defining the precision and quality these printers offer. In this article, we will explore in detail the role and importance of laser technology in this field, the principles of precision design, and the processing workflows involved. We will also focus on methods to enhance production quality using laser profile files. Get ready to discover the potential and advantages of this cutting-edge technology, which prioritizes quality at every stage of industrial applications.
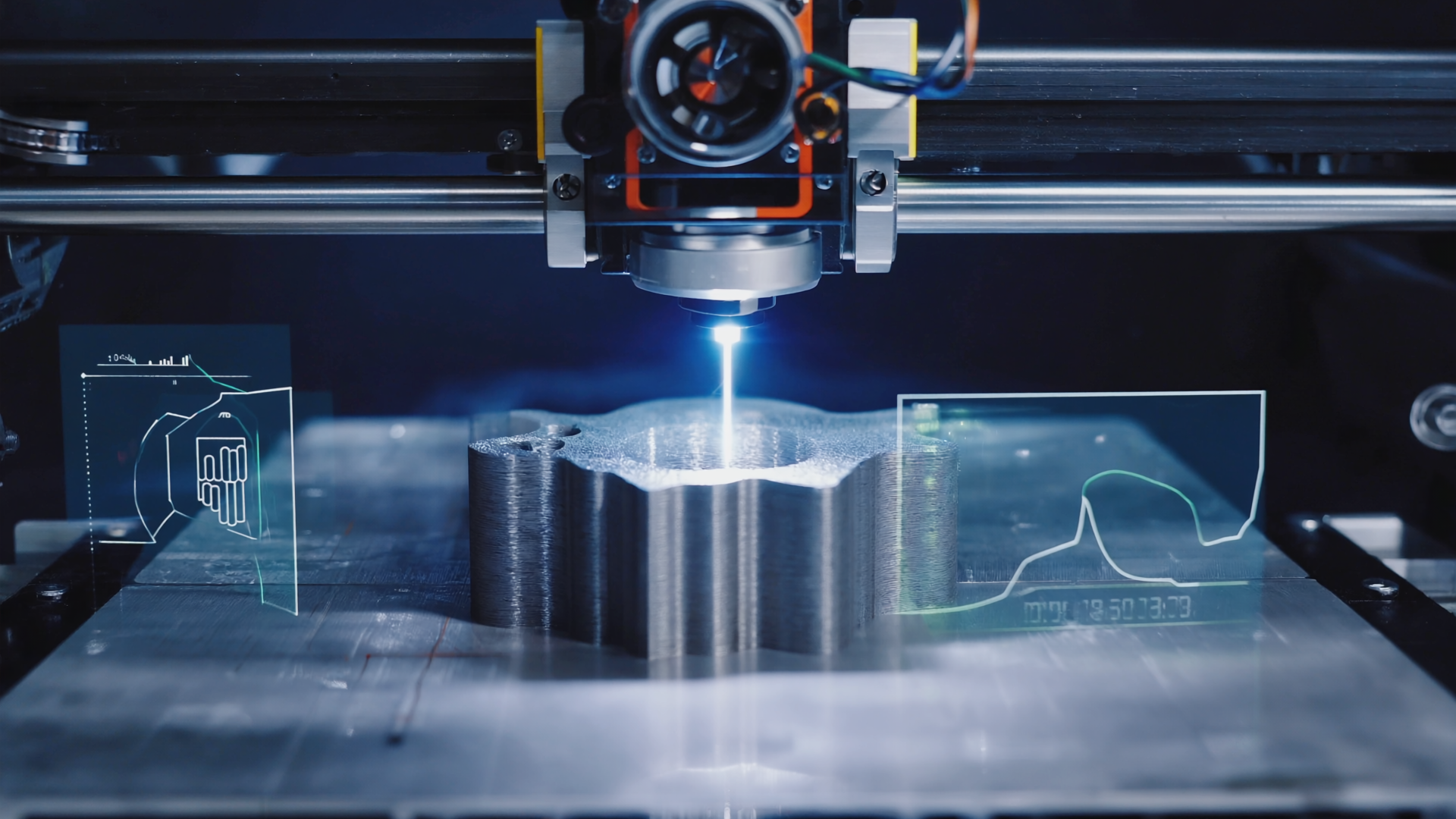
The Role and Importance of Laser Technology in 3D Metal Printers
In 3D metal printers, the laser form and profile file is one of the fundamental elements of the production process. This technology enables the precise layer-by-layer fabrication of metal parts through industrial laser systems. By focusing high energy directly onto the metal powder, laser technology melts the powder and shapes it into the desired form. This process is indispensable, especially for mass production with laser technology, and allows the efficient production of complex metal components.
Successful implementation of this technology also requires integration with the 3D metal printer control system and profile file verification processes. The accurate design and application of the laser form and profile file directly influence product quality. Therefore, perfection in the laser profile file must be rigorously monitored at every stage of production.
Precision Design Principles of Laser Form and Profile Files
The design of laser form and profile files in 3D metal printing is critically important for applications requiring high precision. Key factors to consider in designing these components include material selection, geometric accuracy, and compatibility with integrated systems. The design should be shaped and optimized based on the final use characteristics of the product.
Strict requirements such as profile file verification and tolerance control (0.1 mm) play a central role in the design phases of laser form and profile files. In addition, image processing tolerance control techniques are used to continuously monitor the quality of produced parts.
Industrial laser systems and galvo scanner laser technology enable the creation of form and profile at high speed and accuracy, offering great advantages in rapid prototyping and mass production.
Data obtained from the 3D metal printer control system works in integration with quality control mechanisms throughout the production line. This ensures that products are manufactured to high standards.
Ultimately, the design principles of laser form and profile files go beyond technical details and encompass a comprehensive quality management system. This approach supports the expansion of precision manufacturing technologies.
Laser Form and Profile File Processing Stages in 3D Metal Printers
The processing of laser form and profile files is one of the most critical stages in this technology. The process is managed by the 3D metal printer control system, with every step conducted under detailed scrutiny.
Stage One: Profile file verification. In this stage, the compatibility of the designed laser form with the printer is tested. Advanced image processing methods and industrial laser systems are used to ensure 0.1 mm tolerance control.
Stage Two: Laser form comparison and adjustment. Real-time monitoring detects deviations, and corrections are made using galvo scanner laser technology.
Stage Three: Production optimization. Mass production laser technology and in-line quality control systems come into play. Precision manufacturing technologies are employed to ensure that each layer is accurately built.
Methods to Improve Production Quality with Laser Profile Files
Laser form and profile files are critical factors that directly affect production quality. Profile file verification techniques ensure accuracy within production tolerances.
A properly configured file allows the laser to move optimally across metal surfaces. Image processing tolerance control systems detect deviations and maximize quality control on the production line.
Galvo scanner laser technology enables high-speed operation and tight tolerance control (0.1 mm), offering significant advantages, especially in industries like aerospace and automotive.
Laser profile file optimization should be continuously reviewed within the 3D metal printer control system. Correct implementation enhances both product quality and production efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is the precision of laser form and profile files important in 3D metal printers?
The precision of the laser form and profile file directly affects the quality, durability, and functionality of the final product. Incorrect calibration can lead to surface roughness or structural weaknesses.
How is the precision of laser form and profile files verified?
It is verified through software-based testing and measurements. Parameters such as energy distribution and motion accuracy are analyzed. The laser’s impact is evaluated using simulations.
How is laser calibration performed and how often should it be done?
It is done by adjusting the focal point and power output. It should be repeated during material changes, mechanical updates, or routine maintenance checks.
Which software should be used for profile file precision?
User-friendly software specialized in 3D modeling and simulation should be preferred.
What are the main factors in precision control?
Laser power, focal distance, speed, material response, and environmental conditions (temperature, humidity) should all be considered.
What precautions should be taken during laser system maintenance?
Laser lens cleaning, component wear monitoring, and replacement of worn parts are essential to maintain system performance.
What are the most common precision-related issues?
Focus errors, incorrect power settings, and motion mechanism failures—often due to software or mechanical faults.

